Two Pointers 题目总结
Leetcode 上 Two Pointers tag 的题目基本上有几大类的问题,总结如下。
类型1: 两个指针从两边往中间移动
LeetCode 11. Container With Most Water
想象两个下标 i < j, 如果 height[i] < height[j], 那么是否有必要搜索 [i, j - 1] 这个区间组成的 pair 呢?完全不必。由于 i, j 能接到的水是由短的那个柱子 height[i] 来决定的。如果让 j 向右移动到 i < k < j, 如果 height[i] < height[k] 那 water 仍然是 i 决定的,而且这个面积肯定没有 j 大;如果 height[i] > height[k] 那面积 height[k] * (k - i) 更没有 (i, j) 组成的面积大了。所以这种情况下只需让 i 往右移即可,不需要做重复的搜索。代码:
1 | public class Solution { |
LeetCode 42. Trapping Rain Water
和 Container With Most Water 差不多,原则是从两边往中间去找。原因仍然是接多少水是由比较低的柱子决定的。对左边,记录遇到的最高的柱子leftHeight, 遇到 height[left] <= leftHeight 说明可以接到水,否则让leftHeight = height[left], 右边的柱子同理。代码:
1 | public class Solution { |
LeetCode 167. Two Sum II
非常经典的问题。
类型2: Sliding Window 类
求满足某个条件且长度最长/最短的子数组(窗口类)。这类问题就是枚举起点 i, 如果区间 [i, j] 满足要求,那么下次以 i + 1 为起点时已经知道 [i + 1, j] 已经是满足要求的了,从而避免这段区间的重复的计算。
LeetCode 3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
这是非常经典的窗口类题目。
暴力解法会枚举每个 substring 的起止坐标 (i, j), 但是这个过程中产生了大量的重复计算。我们可以避免重复的搜索,从而把 O(n^2) 的暴力解法优化为 O(n).
举例来说:字符串 “xxxabcdaxxx” 中两个’a’ 的下标分别为 i 和 j, 现在我们知道以 i 开头的最长无重复子串在 [i, j - 1] 区间,并且对于 i 开头的子串,在 [i, j - 1] 这段区间内肯定是没有重复字符的,而且 [i + 1, j - 1], [i + 2, j - 1], … 也都是没有重复字符的。因此我们在下一次查找以 i + 1 开头的字符串时就无需查找 [i + 2, j - 1] 这一段了,因为这段已经确定没有重复了。接下来只需要让 j 往后走扩充这个子串,直到遇到一个子串里已有的字符时停下。
虽然代码里用了嵌套的循环,但时间复杂度是 O(n) 而不是 O(n^2), 原因是 i 和 j 只会往前走,因此数组只遍历了一遍。代码如下:
1 | public class Solution { |
LeetCode 76. Minimum Window Substring
直接上代码:
1 | public class Solution { |
写代码方面的技巧:每次 while 循环退出时 [i, j - 1] 就是符合规则的数组,s[j] 的加入会破坏规则。while 循环条件是 j < s.length() 或者 [i, j] 出现所有字母后时退出。但是当 j == s.length() 时或 [i, j] 出现了所有字母时,退出后有效区间是不同的。前者的有效区间是 [i, j - 1], 后者有效区间是 [i, j]。 怎么解决?在 whlie 循环里判断一下就好了。
LeetCode 209 Minimum Size Subarray Sum
和第 3 题 Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters 的思路非常类似,我们不需要重复的搜索。对于 [i, j] 区间的子数组,如果它到 j 的和 sum 大于等于 s, 那对于 i + 1 开头的子数组,我们只需让 sum = sum - nums[i] 就得到了 [i + 1, j] 的和,然后再让 j 往右走并更新 sum,直到sum >= s,再比较新数组的长度。以上过程避免了重复计算 [i + 1, j] 的和。代码如下:
1 | public class Solution { |
类型3: Partition或QuickSelect
CLRS 里面提供了两种经典的 partition 的方法:Lumuto partition 和 Hoare partition. 两种方法均可以 in-place 地 partition数组 A 从 p 到 r 的部分。值得记下来。
Lomuto Partition
1 | LOMUTO-PARTITION(A, p, r) |
The following figure shows the operation of LOMUTO-PARTITION on a sample array. Array entry A[r] becomes the pivot element x. Lightly shaded array elements are all in the first partition with values no greater than x. Heavily shaded elements are in the second partition with values greater than x. The unshaded elements have not yet been put in one of the first two partitions, and the final white element is the pivot x.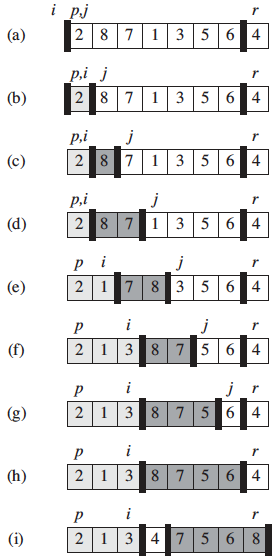
Hoare Partition
Refer to CLRS Problem 7-1: Hoare partition correctness.
1 | HOARE-PARTITION(A, p, r) |
LeetCode 75. Sort Colors
LeetCode 86. Partition List
类型4: 快慢指针
LeetCode 141. Linked List Cycle
一快一慢两个指针。fast 指针每次向前运动两个节点,slow 指针每次向前运动一个节点。如果 fast 和 slow 在链表的某处相遇,则说明链表中有环。
LeetCode 142. Linked List Cycle II
类型5: 数组中的Two Pointers
LeetCode 61. Rotate List
这个是 LinkedList 倒没什么说的。对于翻转数组的话,复习下三步翻转法。
LeetCode 30. Substring with Concatenation of All Words
这个暴力就能过。